Introduction 
fastCNV is an R package that helps you detect, plot and analyse the putative Copy Number Variations (CNVs) in single cell (scRNA-seq) data or Spatial Transcriptomics (ST) data, including Visium HD. Built on SeuratObject, it is easily integrated into scRNA-seq or ST pipelines.
WARNING: Project is still under construction and function usage may change.
Usage
Extensive tutorials to run fastCNVon scRNA-seq and Spatial Transcriptomics data are available to get started here.
NEW : RUN fastCNV ON YOUR VISIUM HD DATA
You can now run fastCNV on visium HD data using fastCNV_10XHD() 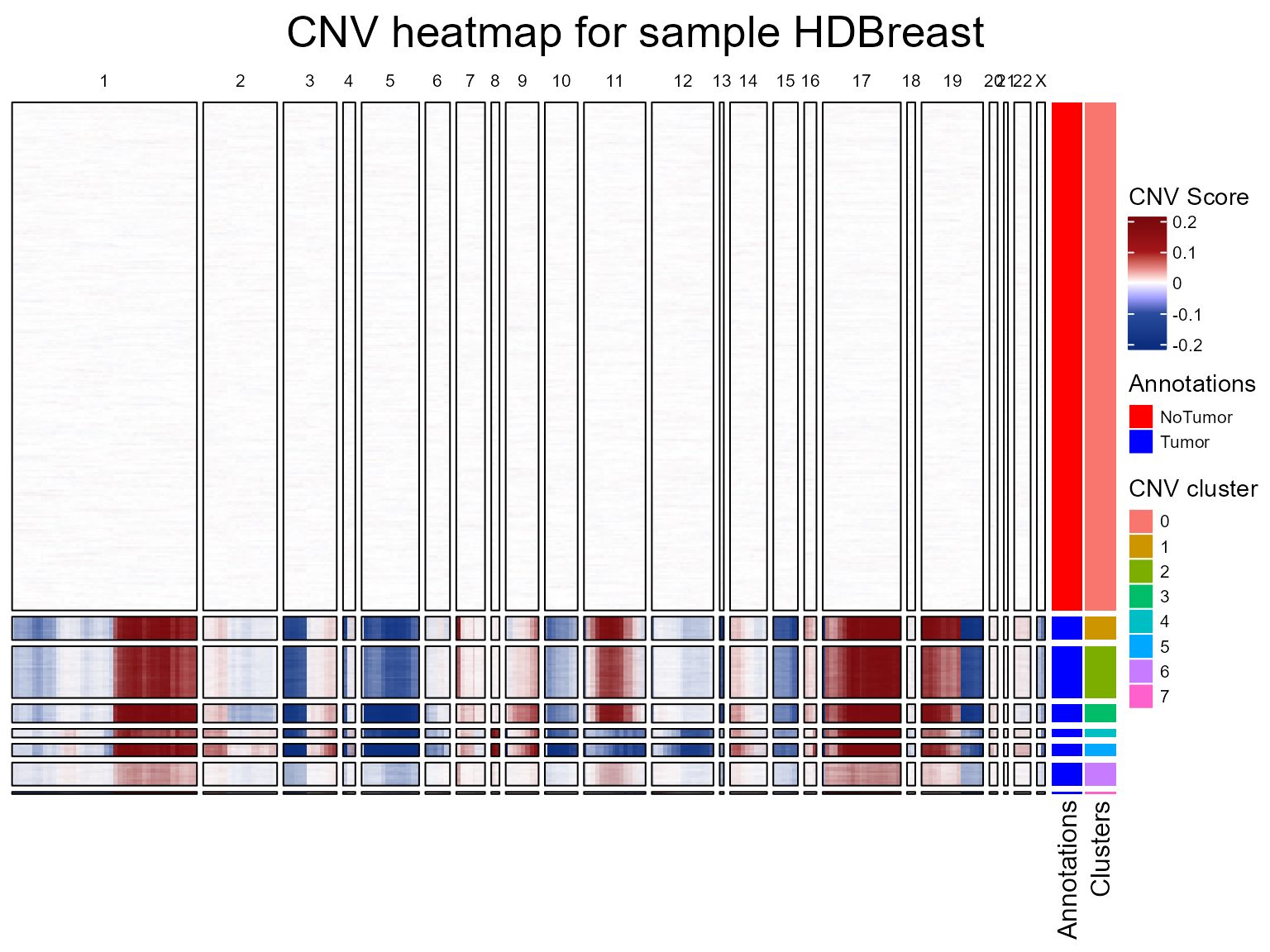
FAQ
1. What kind of data does fastCNV work on?
Currently, fastCNV can be used on scRNA-seq, Visium, and Visium HD data.
2. Does it work on mouse data?
Not yet — fastCNV currently only works on human data. Support for mouse data is in development.
3. How long does it take to run?
It depends on the dataset size and computational resources:
- ~ 1 minute for small scRNA-seq datasets (~4,000 cells)
- ~ 40 minutes for a Visium HD slide at 16 µm resolution (~150,000 spots)
4. I have multiple samples. What’s the fastest way to run fastCNV?
You can process all your samples together by providing fastCNV() with a list of samples, e.g.:
fastCNV(seuratObj = c(sample1, sample2, sample3, ...),
sampleName = c("sample1", "sample2", "sample3", ...),
referenceVar = "Annotations",
referenceLabel = c("Healthy1", "Healthy2", "Healthy3"))5. I have 4 Visium samples, but only one contains healthy tissue. Can I still run them all?
Yes. When you provide a list of samples, fastCNV will pool a reference across all of them, so the healthy tissue from one slide will be used as a reference for all 4 samples.
6. Can I run fastCNV without annotated samples?
Yes, fastCNV can run without a reference.
However, we highly recommend using a healthy reference. If you don’t have one, you can download a healthy sample from a database (same organ, same technology) and use it as reference.
7. What computational resources are required for Visium HD data?
It depends on the bin size:
- 16 µm bin size → ~64 GB RAM is enough
- 8 µm bin size → up to ~200 GB RAM may be required
We are working on reducing the resource requirements.
8. What does the prepareCounts() function do?
This function is designed for Visium samples with low read counts.
It aggregates nearby spots until a threshold is reached (typically 3–4 spots).
Capabilities
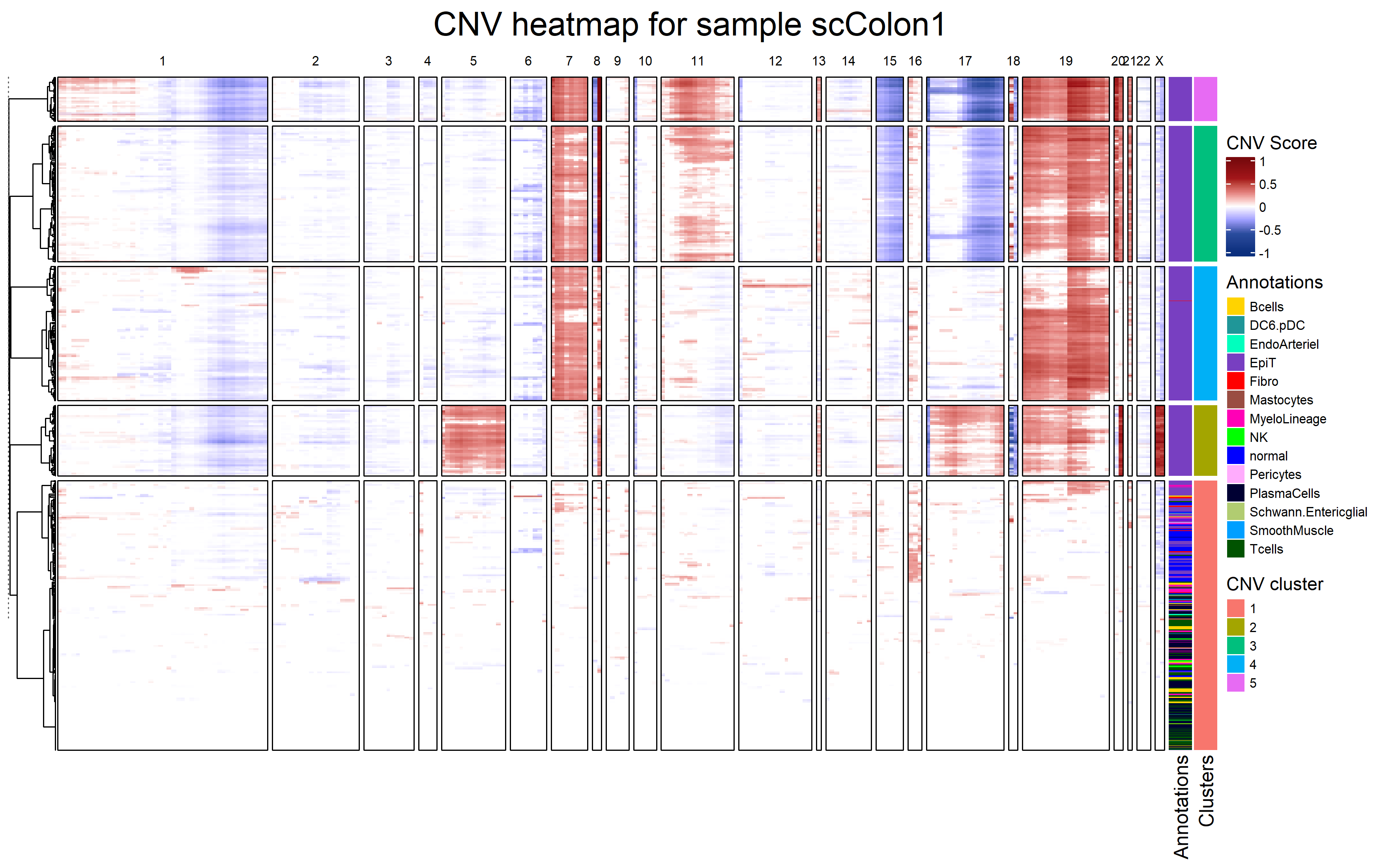
fastCNV can plot a heatmap of inferred CNVs:
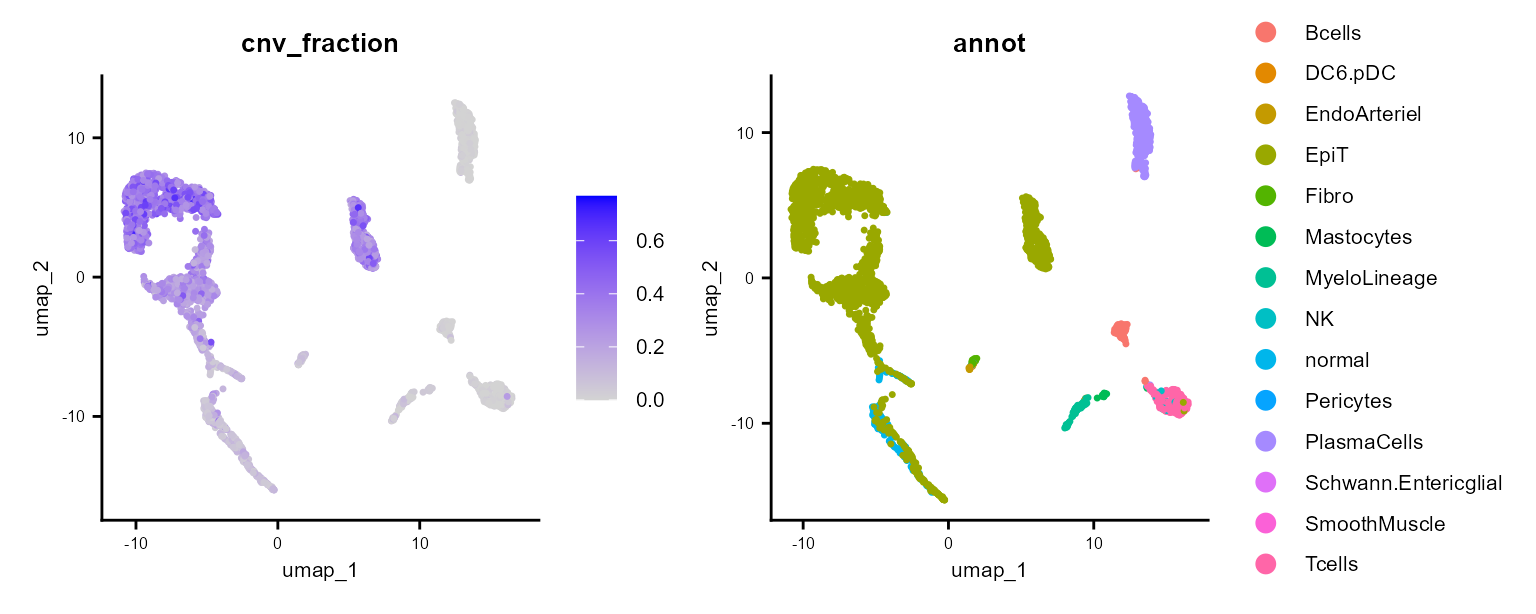
It also calculates a cnv_fraction, which can be plotted with Seurat standard plotting functions:
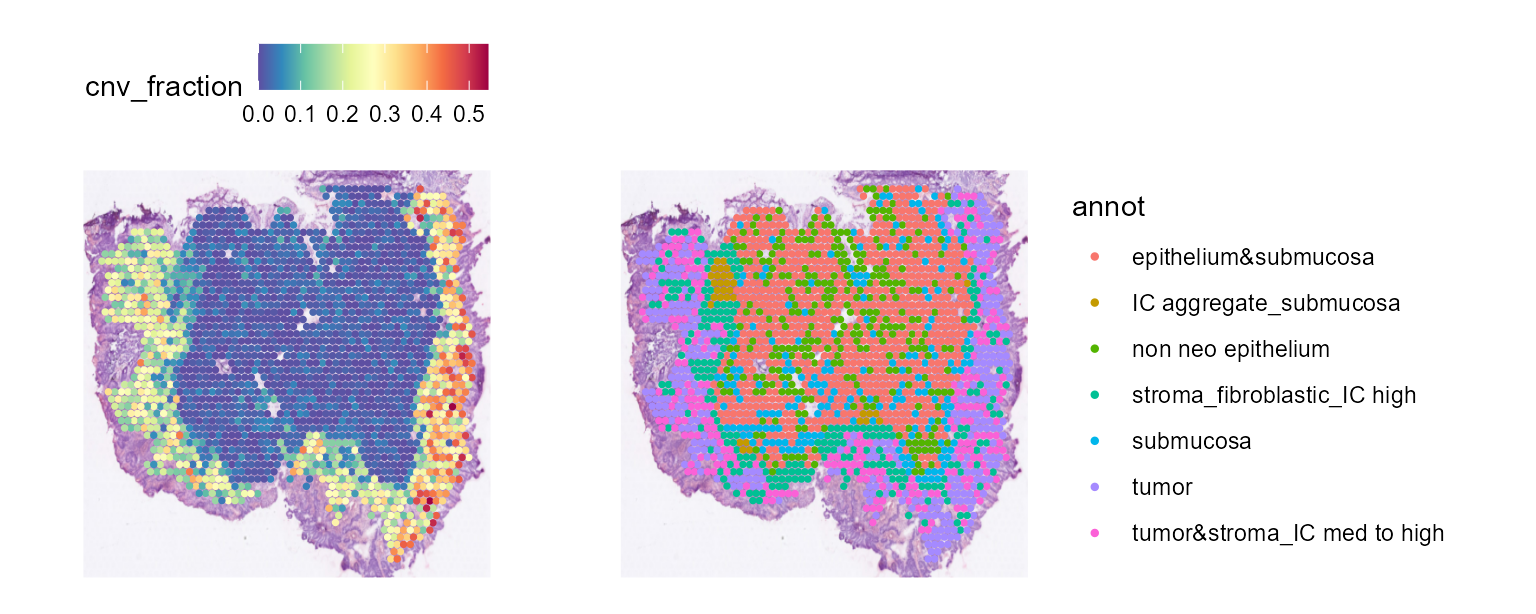
cnv_fractions can also be visualized spatially for Spatial Transcriptomics samples:
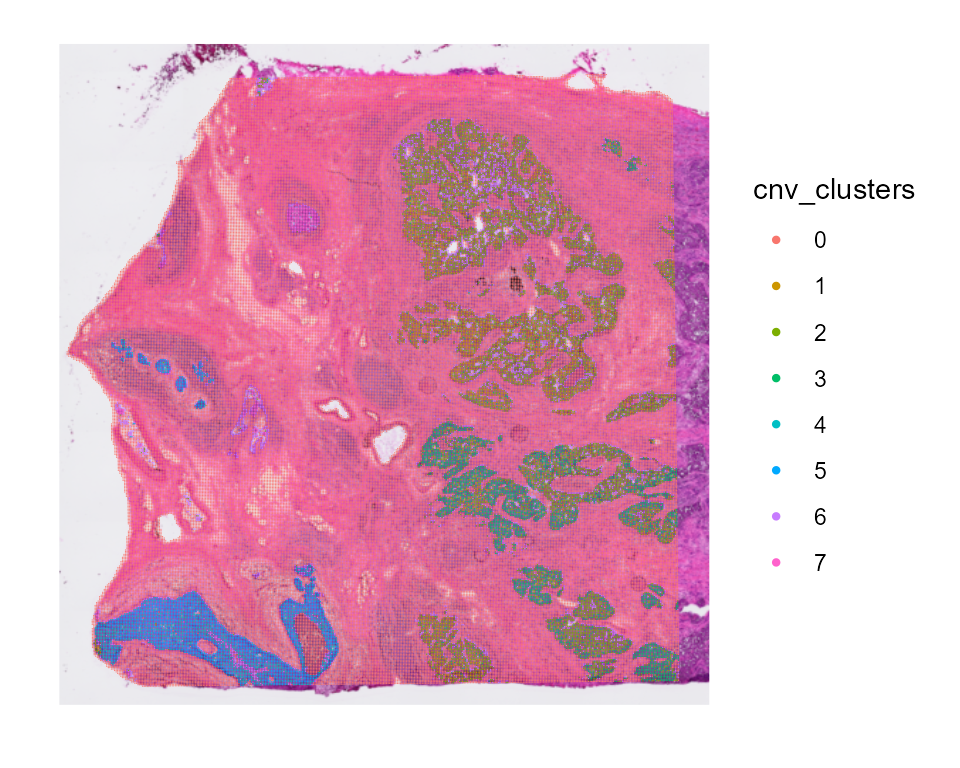
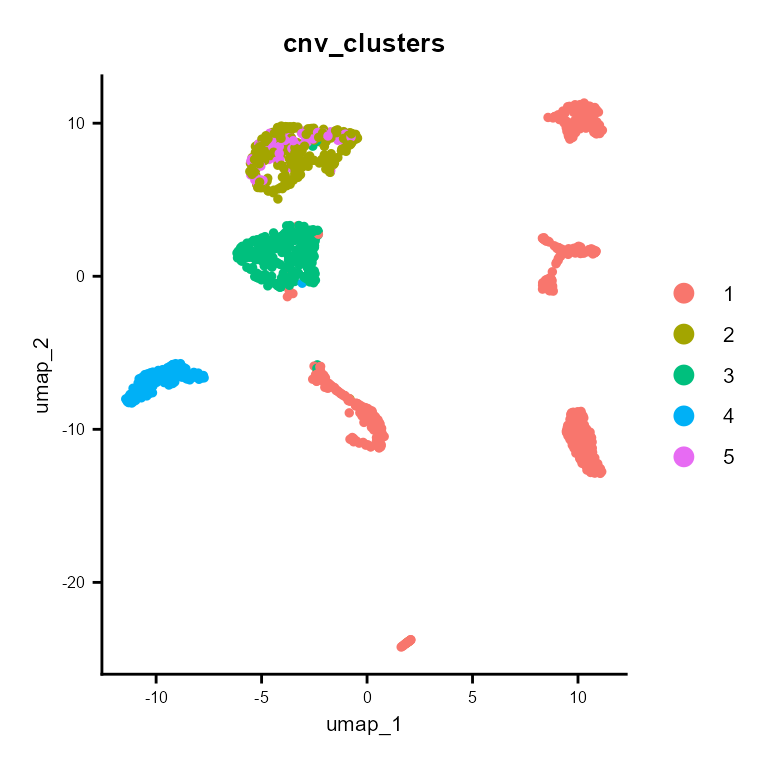
And cnv_fractions can be used to obtain clonal clusters (cnv_clusters):
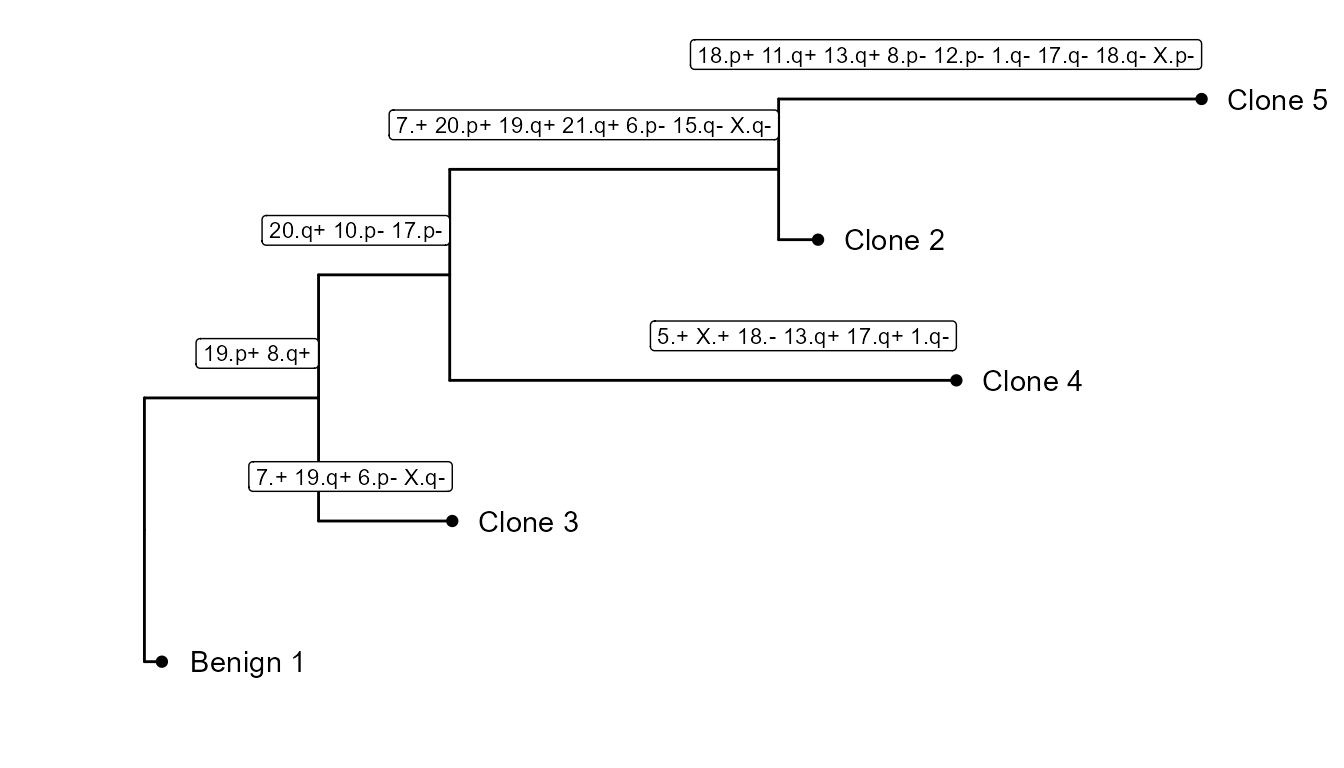
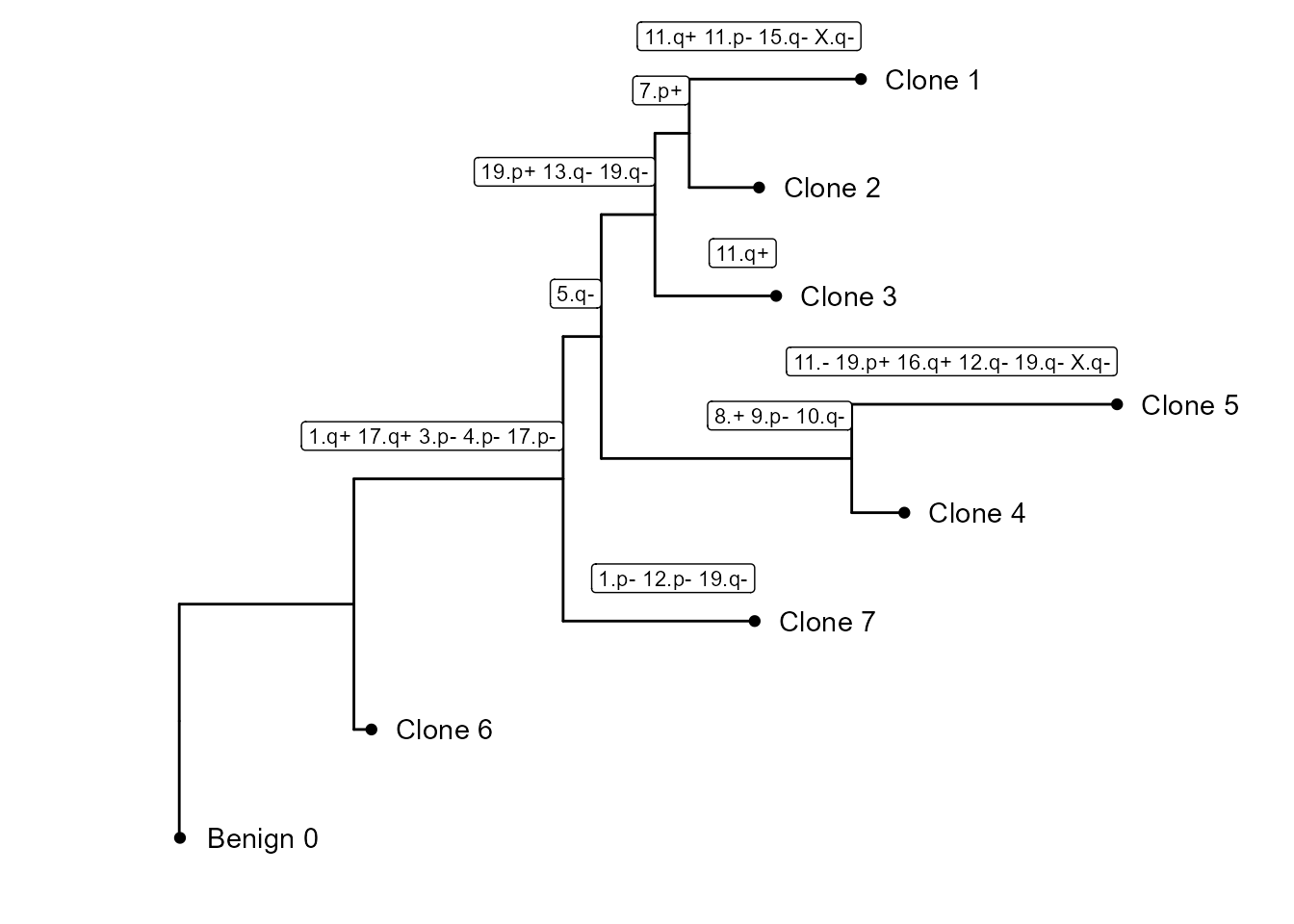
It also builds a subclonality tree based on the CNV clusters: